Fruits you can eat on an animal based diet can be simple, juicy, and honestly pretty satisfying. Many people want animal based diet fruits because they eat mostly meat, eggs, dairy, fish, and still like a little color on the plate. When we choose the best fruits for animal based diet goals like weight loss, better sleep, or stable energy, we pick fruit that is lower in gut irritants, easy to digest, and matched to daily activity. This guide lays out a practical animal based diet fruit list, how much to eat, and how to make fruit work with steak, eggs, and dairy without feeling bloated or foggy.
What an Animal Based Diet Looks Like and Where Fruit Fits
An animal based plan centers on nutrient dense animal foods, then it adds carefully selected plant foods that most people tolerate well. That usually means ripe fruit and sometimes honey in controlled amounts. If you are new, see the core basics here for a quick refresher: Animal Based Diet Guide. Fruit on animal based diet is not a free for all. We pick varieties that keep digestion calm, avoid high oxalate or high histamine triggers, and match carb needs to training or job demands.
In practice, we see fruit doing a few things very well. It supports hydration thanks to water and potassium. It offers vitamin C that beef and eggs have less of. It can make a heavy meat plate feel fresh, which helps appetite control. When we dial fruit correctly, cravings drop, mood feels more even, and recovery from workouts may improve. If we go too hard with fruit, especially dried fruit or juice, you may feel energy crashes, reflux, or bathroom issues. So the goal is balance and timing, not avoidance or overload.
Principles for Choosing Fruit on an Animal Based Diet

To keep digestion calm and energy steady, we use a few rules. These are simple, and they work great for most people in the United States who train or just want steady health and weight control.
- Favor lower fiber, lower seed, easy to chew fruit. Ripe melons and berries usually win here.
- Choose ripe fruit. Unripe fruit can hit the gut harder and taste less sweet anyway.
- Keep portions small to moderate. Start with 1 to 2 palm sized servings a day, not a whole bowl.
- Time fruit near activity or early in the day for better blood sugar management.
- Peel or deseed when sensitive. Removing peels or seeds can lower gut irritation for some folks.
- Prefer whole fruit over juice. Juice spikes hit fast and dont fill you up much.
Animal Based Diet Fruit List
This animal based diet fruit list is sorted by how commonly they fit well with a meat-first approach. We include serving notes, taste cues, and who may benefit most.
Berries: Strawberries, Blueberries, Raspberries, Blackberries
Berries are a go-to because they are lower in sugar per serving, high in water, and rich in vitamin C. Strawberries and blueberries tend to digest gentler for many people. Raspberries and blackberries have more seeds, so individuals with sensitive guts might prefer strawberries most days. Fresh, ripe berries smell sweet, look bright, and dont feel mushy. Pairing a handful of berries with eggs or Greek style yogurt make breakfast feel light but filling. If you notice bloating, reduce portion and test again later.
Melons: Watermelon, Cantaloupe, Honeydew
Melons give hydration and potassium which helps muscles and sleep. Watermelon in summer tastes like cold candy, and many of us remember backyard slices that drip down the wrist. That juicy bite works good after a sweaty workout or on hot days. Cantaloupe and honeydew digest smooth when ripe. Keep pieces small and chew more than you think. A cup with sea salt pinch provides a nice electrolyte hit.
Citrus: Oranges, Clementines, Grapefruit, Lemons, Limes
Orange and clementines are easy to pack for work. Grapefruit offers a bittersweet pop that many people enjoy before steak. Lemons and limes are useful as flavor accents. Citrus membranes can be a little rough for some, so test tolerance. If acid reflux shows up, try mellower fruit like ripe papaya or melon first.
Tropical Options: Papaya, Mango, Pineapple
Papaya is often very gut friendly, especially when orange and soft but not mush. Mango and pineapple taste amazing, but both are sweeter. Pineapple fiber can scratchy the mouth if unripe. For performance days, a small cup of pineapple or mango with a steak and rice free meal can restore muscle glycogen. For rest days, choose papaya or berries to keep carbs more controlled.
Bananas
Bananas are simple and portable. A just ripe banana with light brown specks digest better than green ones for many. Green bananas may spike bloating due to resistant starch. If weight loss is your priority, limit to half a banana or less and pair with a fatty protein source so you stay full longer.
Avocado and Olives
Botanically these are fruit, and they fit neatly into animal based eating. Avocado brings potassium, fiber that usually sits gentle, and creamy texture. Olives add salt and healthy fats. Both are excellent when you want fruit that does not spike glucose much. They help a lot on low carb days where you still want something plant sourced.
Coconut Meat and Coconut Water
Fresh coconut meat is chewy, satisfying, and lower in sugar than sweet fruit. Coconut water has natural electrolytes but can be sugary if you drink a lot. Keep coconut water to a small cup if you need hydration fast after heavy sweat. Coconut flakes in moderation work as a garnish for yogurt paired meals.
Tomatoes and Cucumbers
Technically fruit, though many treat them like vegetables. Some animal based plans include them, some avoid due to nightshade or seed issues. If you tolerate them, peeled and deseeded tomatoes can be easier. Cucumbers are cool and crisp, but seeds may bother sensitive guts. Start small, test response honestly, and keep only what makes you feel good.
Quick Reference Table: Fruit, Carbs, and Suggested Portions
Carb values are rough per 100 grams. Serving sizes are starting points for most active adults. Always adjust by hunger, training, and results.
| Fruit | Carbs per 100 g | Suggested Portion | When To Use | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strawberries | 7 g | 1 cup | Anytime | Gentle on gut, high vitamin C |
| Blueberries | 14 g | 1/2 cup | Pre or post workout | Slightly higher sugar, very tasty |
| Raspberries | 12 g | 1/2 cup | With meals | More seeds may irritate some |
| Watermelon | 8 g | 1 cup | Hot days or post training | Hydrating, add pinch of salt |
| Cantaloupe | 8 g | 1 cup | Breakfast or snack | Easy on stomach when ripe |
| Oranges | 12 g | 1 medium | Morning | Membranes can be tough for some |
| Papaya | 10 g | 1 cup | Anytime | Very gentle, supports digestion feel |
| Mango | 15 g | 1/2 cup | Post workout | Higher sugar, use on active days |
| Pineapple | 13 g | 1/2 cup | Post workout | Acidic in mouth if unripe |
| Banana | 23 g | 1/2 medium | Before training | Choose spotted, not green |
| Avocado | 9 g | 1/2 fruit | Anytime | Mostly fat, very satiating |
| Olives | 6 g | 10 to 12 olives | With meals | Salty, low sugar |
Best Fruits for Animal Based Diet Goals
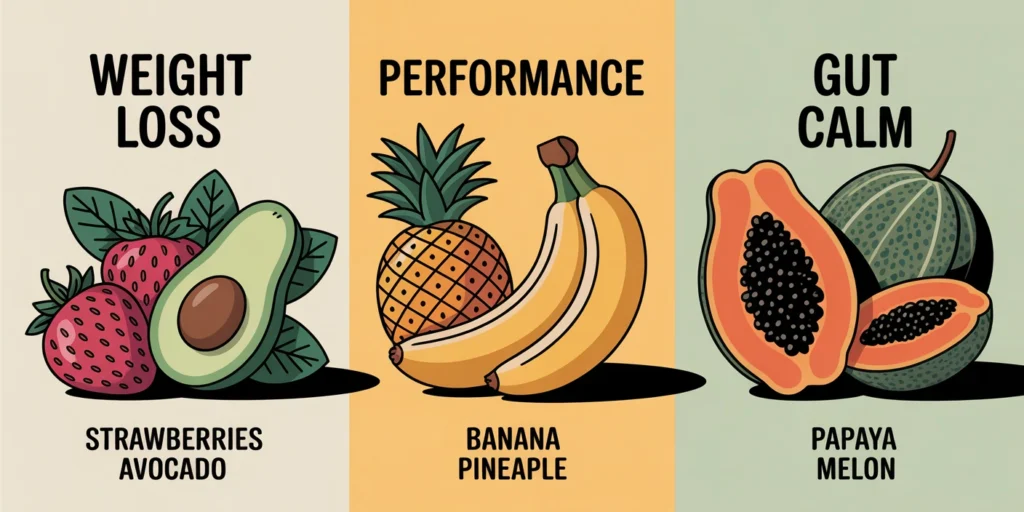
Weight Loss and Satiety
If your main goal is fat loss, fruit should support fullness and steady blood sugar. Papaya, strawberries, cantaloupe, and avocado are favorites. They give volume and texture without a big sugar hit. Eat fruit right after protein so you feel satisfied and less likely to snack later. Pairing a half avocado with eggs or a cup of strawberries with grilled salmon works surprisingly well. For a deeper look at weight management within this style, this guide is useful: Animal Based Diet For Weight Loss.
Performance and Recovery
On days you train hard, a little more sugar helps refill muscle glycogen. Watermelon with sea salt, pineapple, or a small banana can lift performance without making the gut heavy. Keep portions controlled. One palm sized serving before lifting, another small one after, is plenty for most. If you sweat a lot, salt your fruit lightly and drink water. You may notice cramps ease and energy smooth out.
Gut Calm and Sensitivity
When digestion is touchy, choose the softest, ripest fruits and go slowly. Papaya, ripe cantaloupe, peeled and deseeded cucumber, and strawberries tend to sit well. Chew longer, avoid skins and seeds, and keep portions small. Give yourself 2 to 4 weeks to test your response honestly. If a fruit keeps causing issues, park it for now. Your body usually tells the truth fast, we just need to listen better.
Timing, Portions, and Preparation
Fruit timing matters. Many people feel best when they have fruit earlier in the day or around movement. Morning fruit gives quick energy without weighing you down. A short walk after eating helps glucose control and digestion. In the evening, keep fruit modest so sleep does not get disrupted. A few bites of ripe melon after dinner is often fine, but big bowls of fruit can spike energy and bathroom visits.
Portion guidance for most people:
- Weight loss: 1 to 2 servings daily, about 15 to 30 grams of carbs from fruit total.
- Maintenance: 2 to 3 servings daily, about 30 to 50 grams of carbs from fruit.
- Performance days: 3 to 4 smaller servings spread around training, 50 to 80 grams of carbs.
Simple prep tips that make fruit even better:
- Salt your melon. A pinch heightens flavor and improves hydration.
- Pair fruit with protein or fat. Greek style yogurt, cheese, steak, or eggs help blunt glucose spikes.
- Chill fruit for texture. Cold melon or grapes feel refreshing and slow eating pace.
- Peel and deseed when needed. Reduce rough fiber if your stomach gets cranky.
One Week Animal Based Fruit Rotation
This sample rotation keeps variety, manages sugar, and respects training days. Adjust portions to hunger and goals. We keep the rest of the plate animal foods like beef, eggs, seafood, dairy if tolerated, and broths. For guidance on which plants to limit beyond fruit, review: Animal Based Diet Vegetables To Avoid.
Monday: Breakfast eggs with 1 cup strawberries. Dinner ribeye with half avocado. Walk 15 minutes after meals. Sleep usually improves with this combo.
Tuesday: Greek style yogurt with 1/2 cup blueberries. Lunch burger patties and olives. A small orange mid afternoon if energy dips.
Wednesday: Training day. Pre workout half banana and sea salt. Post workout 1 cup watermelon. Dinner salmon and papaya slices.
Thursday: Light day. Cantaloupe cup at breakfast. Avocado with lunch steak. A few olives with cheese as snack if needed.
Friday: Blueberries 1/2 cup in morning. Pineapple 1/2 cup after an afternoon run. Dinner ground beef and simple salad with peeled cucumber if tolerated.
Saturday: Watermelon 1 cup at a cookout. Keep the rest of fruit low. Add yogurt or cottage cheese for satiety.
Sunday: Papaya cup with lime. Roast chicken thighs and olives. Early evening walk to settle the system.
Common Questions About Fruit on Animal Based Diet
Is honey better than fruit?
Both can fit. Honey is pure sugar without fiber, so it hits fast. Fruit comes with water and micronutrients that slow the hit. For most, whole fruit works better day to day, while honey can be kept for workouts or small dessert moments. If your weight loss stalls, scale back honey first.
What about fruit juice?
Juice delivers sugar quickly and lacks fiber. It can be useful for endurance efforts when you need fast carbs. For everyday use, it often spikes and crashes energy. If you love juice, try diluting it 1 to 1 with water and sip slowly with a salty snack. Most of the time, whole fruit wins.
Are dried fruits ok?
Dried fruits are concentrated sugar and can be a little sticky in the gut. They are fine in small amounts on long hikes or during heavy training, but they are very easy to overeat at home. Keep dried fruit as a tool, not a daily habit.
How do I know if fruit is causing me issues?
Track hunger swings, bloating, skin reactions, and sleep. If a fruit repeatedly brings cramps or brain fog, reduce it or remove for a couple weeks. Bring it back in a small portion later and see if things calm down. Slow, steady tests beat guessing.
Mistakes To Avoid With Animal Based Diet Fruits
We see the same traps again and again. You can skip them and save months of frustration.
- Grazing on fruit all day. This keeps insulin elevated and may stall fat loss.
- Eating unripe fruit. Hard, sour fruit can upset digestion and taste worse.
- Big fruit bowls at night. Sleep can get lighter, and midnight hunger shows up.
- Forgetting salt and water. Hydration makes fruit feel better and reduces cramps.
- Adding fruit to already heavy carb meals. Pair fruit with protein and fat instead.
- Ignoring personal tolerance. Your buddy loves blackberries, your gut says no thanks.
A Practical Shopping and Storage Game Plan
Buy fruit twice a week so it stays fresh. Pick heavy, fragrant melons with a creamy yellow field spot. Strawberries should be bright, dry, and without mushy spots. Store berries dry in a ventilated container and wash right before eating so they last longer. Let bananas ripen with freckles before you use them for smoother digestion. Keep citrus in the fridge drawers, it keeps flavor snappy for days. If money is tight, frozen berries are an amazing buy and often higher in nutrients than sad out of season berries.
How Fruit Complements the Animal First Plate
An animal based diet centers around proteins and healthy fats that bring iron, zinc, B vitamins, and complete amino acids. Fruit adds freshness, color, hydration, and specific micronutrients like vitamin C and potassium. We do not need tons of fruit, just enough to support our life. The combo of steak or eggs plus a little fruit often flips cravings off like a switch, which make life way easier. Simple cooking, simple shopping, better meals.
Personal Note On Enjoyment and Sustainability
Food should taste good and feel good. The snap of a cold grape on a July afternoon, the sweet drip of watermelon at a park bench, the comfort of strawberries over creamy yogurt after a long workday. These moments matter. They keep a plan sustainable. If you allow small fruit servings that you truly enjoy, you are far more likely to stick with animal based eating month after month. Consistency beat perfection every single time.
If you want to tighten your structure, revisit the fundamentals and build your weekly template from here: https://dietlinic.com/animal-based-diet/. Use it as a map, then fit the fruit choices that work best for your body and schedule.
Bottom Line: Fruits You Can Eat on an Animal Based Diet
Fruit on animal based diet should be deliberate, tasty, and matched to goals. Start with strawberries, blueberries, watermelon, cantaloupe, papaya, oranges, avocado, and olives. Time your portions near activity, keep serving sizes modest, and pair fruit with animal protein or fat to control blood sugar. Skip the constant snacking and keep juice and dried fruit rare. With a smart animal based diet fruit list, your meals feel balanced, energy stays more steady, and health moves the right way without making food complicated. For more structure and ideas that fit this style, you can also read: Animal Based Diet For Weight Loss.
Fruits you can eat on an animal based diet are many when you choose wisely. Build your own list, pay attention to digestion and mood, and adjust portions week by week. That is how most of us find the best fruits for animal based diet results that actually last.








Leave a Reply